ADHD, Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Distorter occurs in about 3-7% of school aged children. It effects their ability to progress social, occupational, or academically. It also must be present before the age of 7 and occur in at least to different settings. Although the name suggests inattention, many children with ADHD have long attention spans toward activities they find interesting.

Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Distorter is more commonly diagnosed in males than females. 30-50% of those diagnosed continue to have issues into adulthood. Common symptoms include:
- Struggles to follow directions
- Easily distracted
- Seems to not be listening
- Daydreaming
- Problems processing information quickly and accurately
- Problems maintaining focus
- Becomes bored easily
- Troubles completing and/or turning in assignments
May also include: Fidgeting, talking nonstop, impulsive, not able to sit still, difficulty doing quiet tasks, not able to wait turn, emotional, touching and playing with everything in sight

The cause of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Distorter is unknown. It is believed to be a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Many of the genes effected seem to be connected to the dopamine neurotransmitters. Environmental factors can include alcohol and tobacco use during pregnancy, lead and insecticide exposure, premature and/or low birth weight and brain injury.
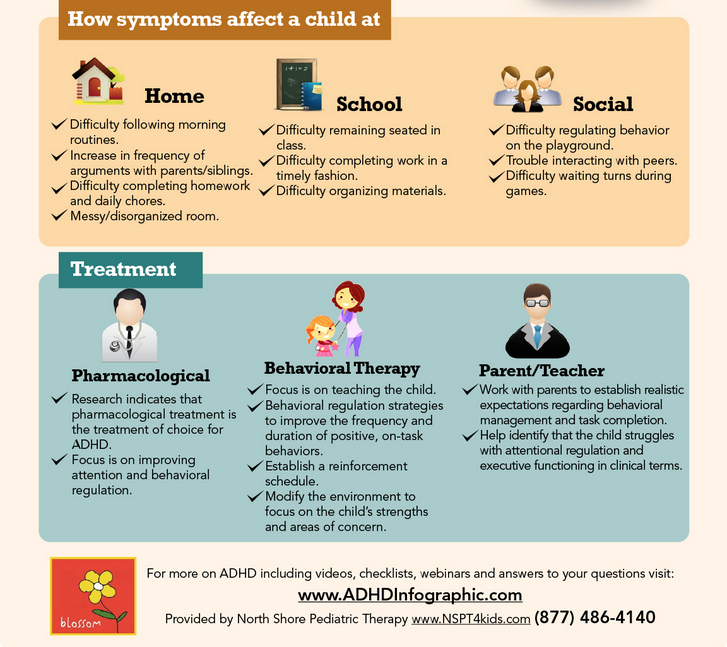
If these symptoms sound like your child, talk to your pediatrician. Medication and therapy can be used as treatment.
Articles related to ‘ADHD What You Need to Know’
ADHD: Fact, Fiction, and What Can Help